Table of contents
1
Macronutrients - what they are and why we need them
2
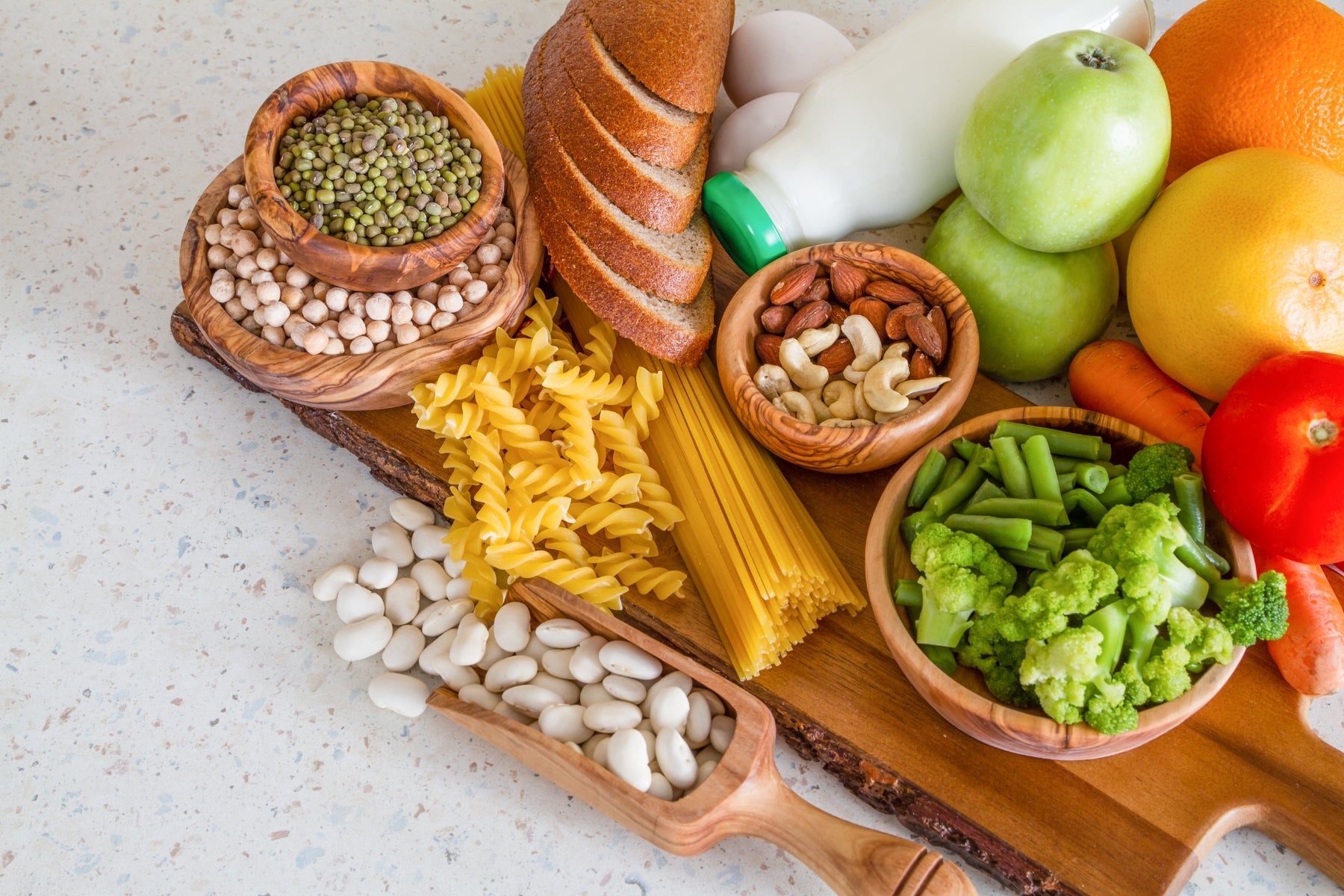
Carbohydrates
3
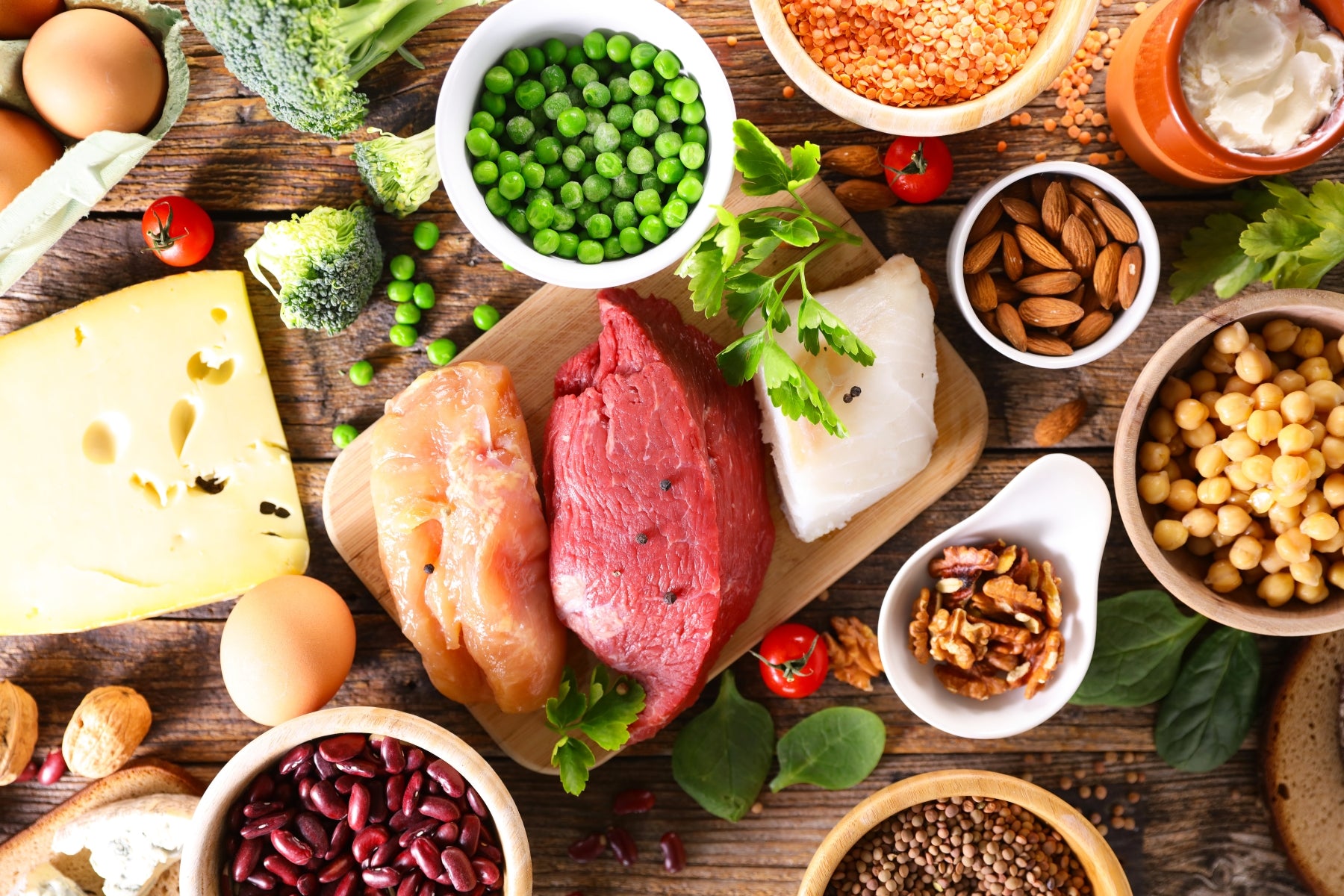
Protein
4
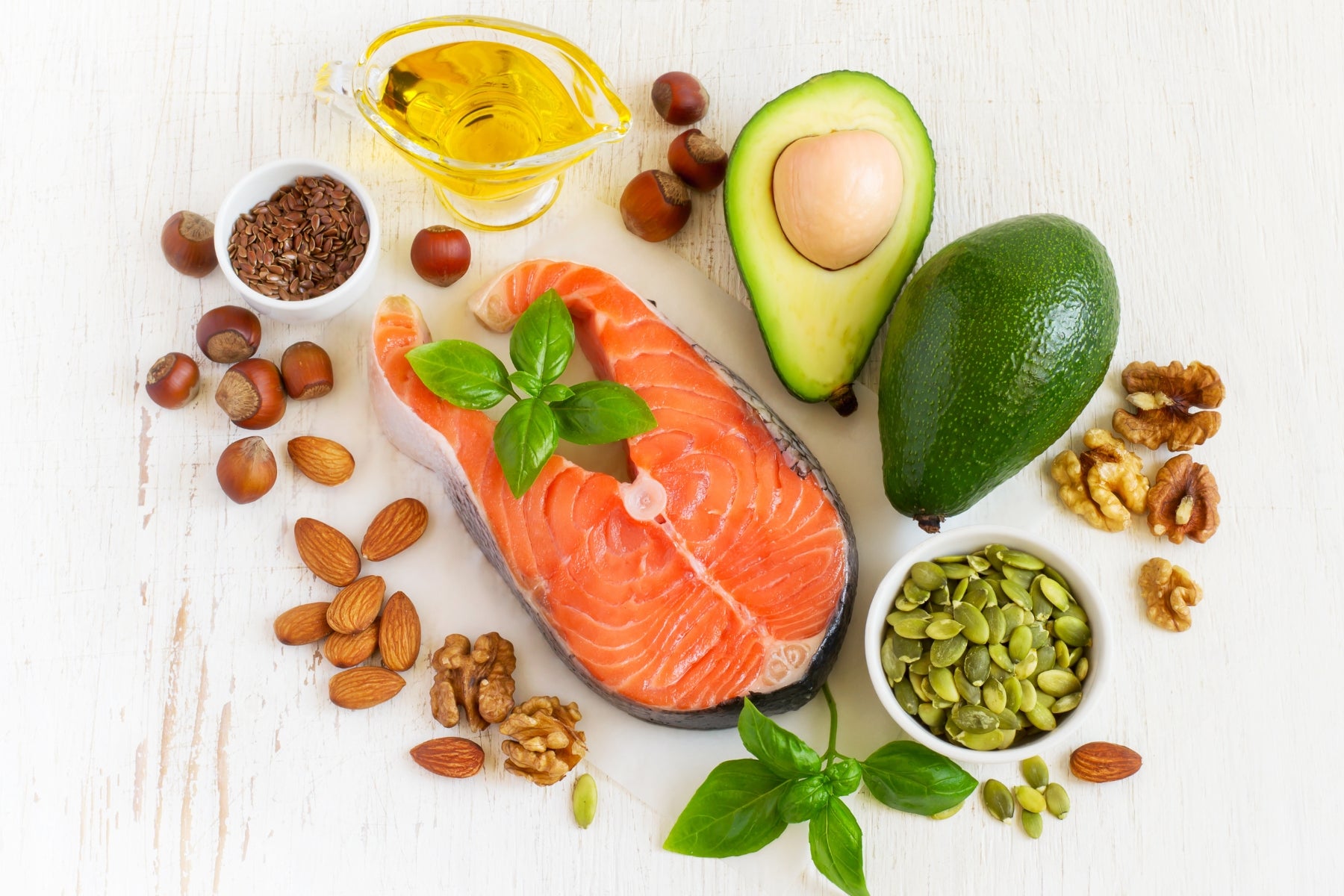
Fats
5
Fiber
6
Ausgewogene Ernährung
7
Optimize macronutrient intake with drinking meals
Table of contents
1
Macronutrients - what they are and why we need them
2
Carbohydrates
3
Protein
4
Fats
5
Fiber
6
Ausgewogene Ernährung
7
Optimize macronutrient intake with drinking meals